UK nations and regions
South East England
With its proximity to London and major international airports and ports, South East England provides a competitive edge for both domestic and international trade, offering a vibrant ecosystem for innovation, and a large, growing economy.
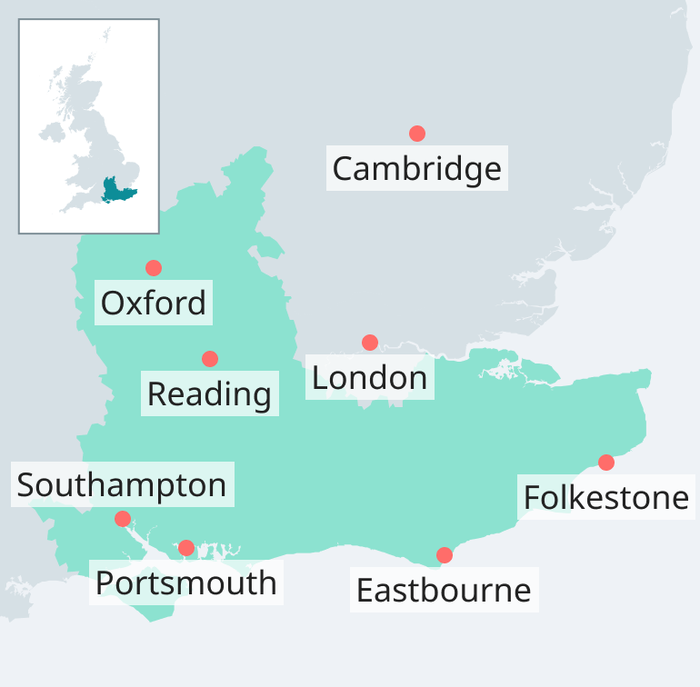
With 18 universities retaining 56% of graduates annually, South East England benefits from a highly skilled workforce. The Thames Valley serves as a major innovation hub for technology, life sciences, and creative industries. As the UK's largest and most productive regional economy outside London, it has the fastest forecast growth across diverse sectors including services, manufacturing, aerospace, and emerging technologies.
Key facts for the South East
£350 million investment fund from The British Bank in 2026
£6.5 billion transport investment
85 foreign direct investment projects in 2024 to 2025
21% of the UK’s total exports
Space cluster largest in the UK
16 universities
An industrial strategy for the whole of the UK
The modern Industrial Strategy is a new economic approach – a whole-of-government effort to back the UK’s strengths, with ambitious plans for 8 high-growth sectors (‘IS-8’) and the frontier industries at their leading edge, from quantum to pharmaceuticals. It is a 10-year plan, built on stability and openness, to make the UK the best country to invest in.
Building on the South East's strengths
The South East already has a huge amount to celebrate and the Industrial Strategy’s Sector Plans promote its wide-ranging strengths to investors.
Advanced manufacturing
Anchored by Oxford’s world-leading university, the Oxford-Cambridge Growth Corridor comprises spinouts in graphene and batteries and home to BMW Mini, Oxford Instruments, Fortescue Zero, Lockheed Martin, and Oxford Space Systems.

Clean energy industries
The UK Atomic Energy Authority (UKAEA) in Culham, Oxfordshire, leads on Fusion R&D with a new fuels partnership with Eni, while Project Brunel has invested £14.6 million in hydrogen engines. The offshore wind sector as a whole is actively seeking to attract investment into South East region, with the Offshore Wind Industry Council estimating demand for around £287 million to £630 million investment in the South East alone to achieve the priorities in their Regional Growth Prospectus.

Digital and technologies
Home to the world-leading University of Oxford, Oxfordshire is host to the Culham AI Growth Zone, Harwell Science & Innovation Campus and National Quantum Computing Centre. Its key R&D companies include Oxford Instruments, Sophos and Oxford Ionics.
Defence
The region is home to strengths across the Oxford to Cambridge Growth Corridor and in Portsmouth and the Solent.
- The Oxford to Cambridge Growth Corridor has strengths in space, AI, quantum technologies, cyber, engineering biology, semiconductors and advanced connectivity technologies. The Corridor is a world-leading arc for innovation cohered around renowned universities and the cutting-edge Harwell Campus site, which hosts the National Quantum Computing Centre
- Portsmouth and the Solent has strengths in space, drones and autonomous systems. QinetiQ's National Maritime Systems Centre and the National Oceanography Centre are at the forefront of marine science and technology, including on autonomous and robotic underwater systems. Home to HMNB Portsmouth and Solent Freeport, this is a key maritime hub

Financial services
Swindon, Brighton, Bournemouth and East Surrey have strengths in insurance, asset management and fintech. Companies such as Zurich operate in Swindon and JP Morgan has technology offices in Bournemouth. These locations benefit from strong transport links to London, major international airports like Gatwick, and deep talent pools to tap into, with access to a high-quality professional business eco-system, and offers prospective talent high-living standards with easy access to London.
Life sciences
The Oxford-Cambridge Growth Corridor is a leader in R&D, translational medicine and AI adoption for healthcare outcomes, with an extensive talent, incubator, venture capital (VC), advisory and science park network. It is anchored by world-leading universities, NHS teaching hospitals and global pharma firms such as Moderna and Novo Nordisk.

Foundational industries relevant to IS-8 supply chains
The South East has a number of ports, such as the Solent Freeport, and a construction industry.

Driving regional growth in the South East
The Industrial Strategy introduces ambitious policies to drive growth and investment across every nation and region of the UK. This is a 10-year strategy which will be a living document. We want to continue to work with local government, mayoral strategic authorities and devolved governments to ensure they can drive growth across the UK.
More policies will be delivered over time, but below are some of the specific interventions in the South East that form part of our strategy.
Locally targeted investments in the IS-8 growth driving sectors
An AI Growth Zone in Culham to facilitate AI infrastructure and unlock investment in AI-enabled data centres.
Devolved funding for the local leaders who know their places best to help deliver their Local Growth Plans
- Enhanced support for Solent Freeport, specialised in Advanced Manufacturing and Clean Energy Industries, with streamlined planning processes, better-targeted investment promotion, support for accessing concessionary finance, and coordinated support on skills
Tools to help city regions and clusters attract private investment
- The British Business Bank will expand their Nations and Regions Investment Funds with £350 million to cover the South East for the first time
Backing the Oxford to Cambridge Growth Corridor via major housing and infrastructure projects
- East-West Rail, a major new cross-country rail line cutting journey times significantly between Oxford and Cambridge. This will enable delivery of up to 100,000 new homes, create thousands of new jobs by expanding the commuting populations of economic centres across the corridor, and add £6.7 billion a year to regional Gross Value Added (GVA) by 2050. The first phase will launch later this year and enable direct rail travel between Oxford and Milton Keynes for the first time in nearly 60 years. A new East Coast Mainline station at Tempsford, integrating the Corridor into one of the UK's busiest rail routes between London to Edinburgh
- Ensuring that water companies build new reservoirs in areas around Cambridge (the Fens) and Oxford (Abingdon) so that industrial and residential developments are not held back due to pressures on water availability
- Strengthening the region's science and technology credentials through the UK's first AI Growth Zone in Culham, Oxfordshire, confirmed as the first site for our new flagship programme to facilitate AI infrastructure and unlock investment in AI-enabled data centres
- Exploring how to strengthen collaboration between the Oxford Cambridge Growth Corridor and other parts of the UK with complementary strengths. This will build on recent government investment in the Cambridge-Manchester Innovation Partnership
- Addressing the shortage of high-quality research facilities driven by consistently high demand for R&D space. We will fund the Cambridge Growth Company to invest in infrastructure to unlock housing and commercial development, enter into partnerships with the private sector, and work with local partners on infrastructure delivery, with more details to be set out shortly. The Oxford Growth Commission will also develop a long-term investment strategy
- Cambridgeshire and Peterborough will benefit from a £38 million Local Transport Grant between 2026/27 and 2029/30, which enables local authorities to deliver transport improvements including more zero emission buses, cycleways, accessibility and congestion improvement measures